This section provides a comprehensive overview of the legacy microservices within the United Manufacturing Hub. These microservices are currently in a transitional phase, being maintained and deployed alongside newer versions of UMH as we gradually shift from Data Model v1 to v2. While these legacy components are set to be deprecated in the future, they continue to play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations and compatibility during this transition period.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Legacy
- 1: Factoryinput
- 2: Grafana Proxy
- 3: Kafka Bridge
- 4: Kafka State Detector
- 5: Kafka to Postgresql
- 6: MQTT Bridge
- 7: MQTT Kafka Bridge
- 8: MQTT Simulator
- 9: MQTT to Postgresql
- 10: OPCUA Simulator
- 11: PackML Simulator
- 12: Tulip Connector
- 13: Grafana Plugins
- 13.1: Umh Datasource
- 13.2: Factoryinput Panel
1 - Factoryinput
This microservice is still in development and is not considered stable for production use
Factoryinput provides REST endpoints for MQTT messages via HTTP requests.
This microservice is typically accessed via grafana-proxy
How it works
The factoryinput microservice provides REST endpoints for MQTT messages via HTTP requests.
The main endpoint is /api/v1/{customer}/{location}/{asset}/{value}, with a POST
request method. The customer, location, asset and value are all strings. And are
used to build the MQTT topic. The body of the HTTP request is used as the MQTT
payload.
What’s next
- Read the Factoryinput reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the Factoryinput microservice.
2 - Grafana Proxy
This microservice is still in development and is not considered stable for production use
How it works
The grafana-proxy microservice serves an HTTP REST endpoint located at
/api/v1/{service}/{data}. The service parameter specifies the backend
service to which the request should be proxied, like factoryinput or
factoryinsight. The data parameter specifies the API endpoint to forward to
the backend service. The body of the HTTP request is used as the payload for
the proxied request.
What’s next
- Read the Grafana Proxy reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the Grafana Proxy microservice.
3 - Kafka Bridge
Kafka-bridge is a microservice that connects two Kafka brokers and forwards messages between them. It is used to connect the local broker of the edge computer with the remote broker on the server.
How it works
This microservice has two ways of operation:
- High Integrity: This mode is used for topics that are critical for the user. It is garanteed that no messages are lost. This is achieved by committing the message only after it has been successfully inserted into the database. Ususally all the topics are forwarded in this mode, except for processValue, processValueString and raw messages.
- High Throughput: This mode is used for topics that are not critical for the user. They are forwarded as fast as possible, but it is possible that messages are lost, for example if the database struggles to keep up. Usually only the processValue, processValueString and raw messages are forwarded in this mode.
What’s next
- Read the Kafka Bridge reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the Kafka Bridge microservice.
4 - Kafka State Detector
How it works
What’s next
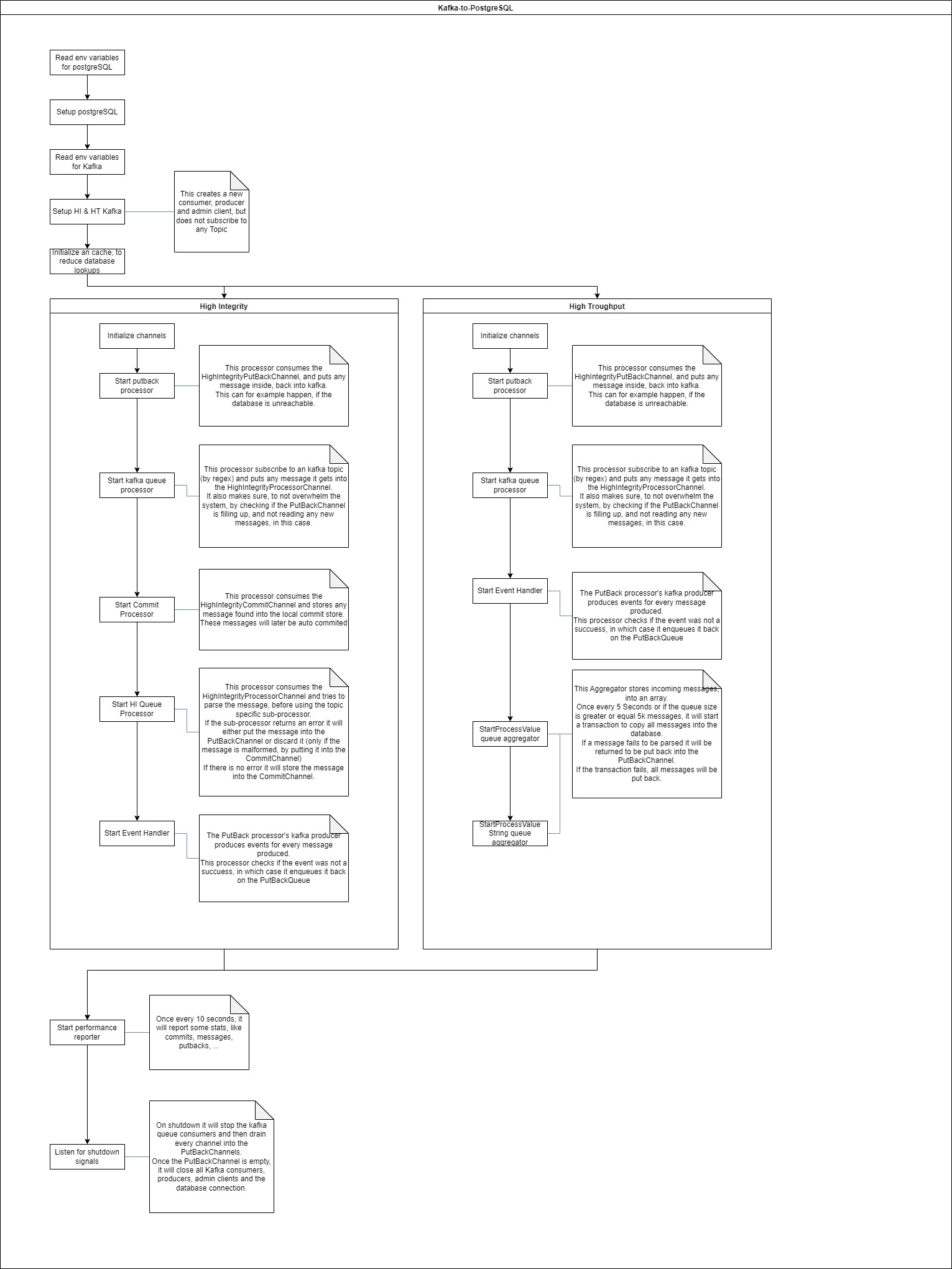
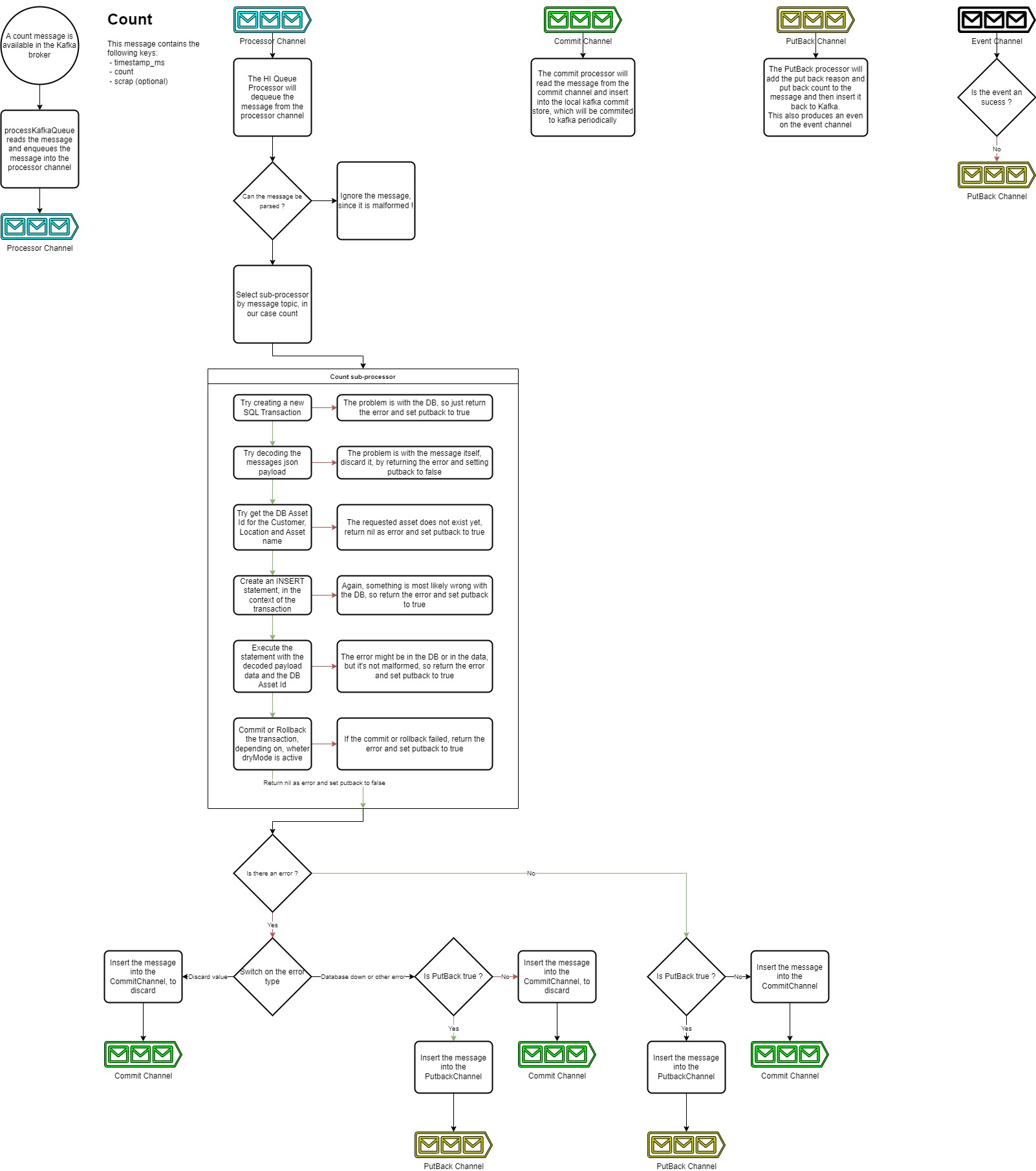
5 - Kafka to Postgresql
Kafka-to-postgresql is a microservice responsible for consuming kafka messages and inserting the payload into a Postgresql database. Take a look at the Datamodel to see how the data is structured.
This microservice requires that the Kafka Topic umh.v1.kafka.newTopic exits. This will happen automatically from version 0.9.12.
How it works
By default, kafka-to-postgresql sets up two Kafka consumers, one for the High Integrity topics and one for the High Throughput topics.
The graphic below shows the program flow of the microservice.
High integrity
The High integrity topics are forwarded to the database in a synchronous way. This means that the microservice will wait for the database to respond with a non error message before committing the message to the Kafka broker. This way, the message is garanteed to be inserted into the database, even though it might take a while.
Most of the topics are forwarded in this mode.
The picture below shows the program flow of the high integrity mode.
High throughput
The High throughput topics are forwarded to the database in an asynchronous way. This means that the microservice will not wait for the database to respond with a non error message before committing the message to the Kafka broker. This way, the message is not garanteed to be inserted into the database, but the microservice will try to insert the message into the database as soon as possible. This mode is used for the topics that are expected to have a high throughput.
The topics that are forwarded in this mode are processValue, processValueString and all the raw topics.
What’s next
- Read the Kafka to Postgresql reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the Kafka to Postgresql microservice.
6 - MQTT Bridge
MQTT-bridge is a microservice that connects two MQTT brokers and forwards messages between them. It is used to connect the local broker of the edge computer with the remote broker on the server.
How it works
This microservice subscribes to topics on the local broker and publishes the messages to the remote broker, while also subscribing to topics on the remote broker and publishing the messages to the local broker.
What’s next
- Read the MQTT Bridge reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the MQTT Bridge microservice.
7 - MQTT Kafka Bridge
Mqtt-kafka-bridge is a microservice that acts as a bridge between MQTT brokers and Kafka brokers, transfering messages from one to the other and vice versa.
This microservice requires that the Kafka Topic umh.v1.kafka.newTopic exits.
This will happen automatically from version 0.9.12.
Since version 0.9.10, it allows all raw messages, even if their content is not in a valid JSON format.
How it works
Mqtt-kafka-bridge consumes topics from a message broker, translates them to the proper format and publishes them to the other message broker.
What’s next
- Read the MQTT Kafka Bridge reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the MQTT Kafka Bridge microservice.
8 - MQTT Simulator
This microservice is a community contribution and is not part of the main stack of the United Manufacturing Hub, but is enabled by default.
The IoTSensors MQTT Simulator is a microservice that simulates sensors sending data to the MQTT broker. You can read the full documentation on the
How it works
The microservice publishes messages on the topic ia/raw/development/ioTSensors/,
creating a subtopic for each simulation. The subtopics are the names of the
simulations, which are Temperature, Humidity, and Pressure.
The values are calculated using a normal distribution with a mean and standard
deviation that can be configured.
What’s next
- Read the IoTSensors MQTT Simulator reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the IoTSensors MQTT Simulator microservice.
9 - MQTT to Postgresql
If you landed here from Google, you probably might want to check out either the architecture of the United Manufacturing Hub or our knowledge website for more information on the general topics of IT, OT and IIoT.
This microservice is deprecated and should not be used anymore in production. Please use kafka-to-postgresql instead.
How it works
The mqtt-to-postgresql microservice subscribes to the MQTT broker and saves
the values of the messages on the topic ia/# in the database.
What’s next
- Read the MQTT to Postgresql reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the MQTT to Postgresql microservice.
10 - OPCUA Simulator
This microservice is a community contribution and is not part of the main stack of the United Manufacturing Hub, but is enabled by default.
How it works
The OPCUA Simulator is a microservice that simulates OPCUA devices. You can read the full documentation on the GitHub repository.
You can then connect to the simulated OPCUA server via Node-RED and read the values of the simulated devices. Learn more about how to connect to the OPCUA simulator to Node-RED in our guide.
What’s next
- Read the OPCUA Simulator reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the OPCUA Simulator microservice.
11 - PackML Simulator
This microservice is a community contribution and is not part of the main stack of the United Manufacturing Hub, but it is enabled by default.
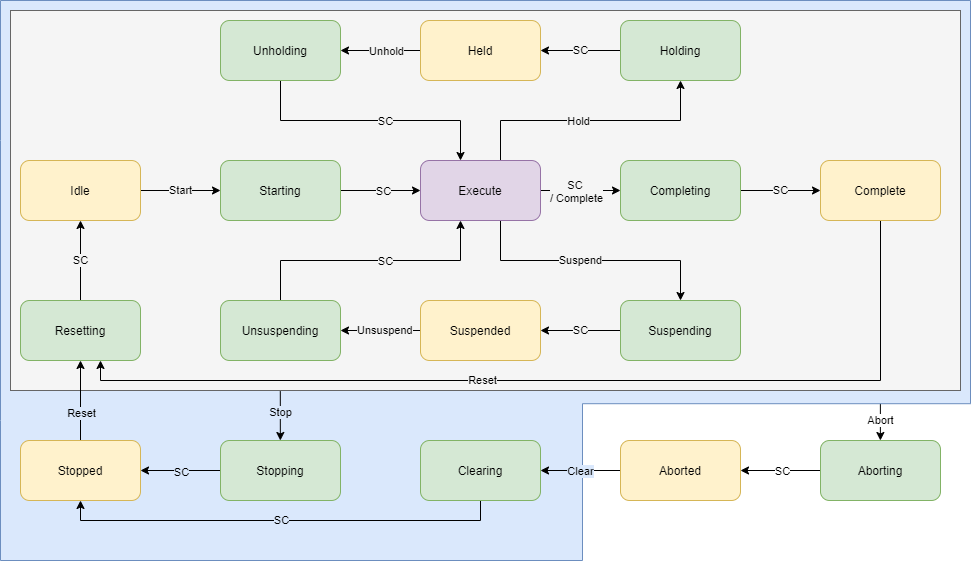
PackML MQTT Simulator is a virtual line that interfaces using PackML implemented over MQTT. It implements the following PackML State model and communicates over MQTT topics as defined by environmental variables. The simulator can run with either a basic MQTT topic structure or SparkPlugB.
How it works
You can read the full documentation on the GitHub repository.
What’s next
- Read the PackML Simulator reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the PackML Simulator microservice.
12 - Tulip Connector
This microservice is still in development and is not considered stable for production use.
The tulip-connector microservice enables communication with the United Manufacturing Hub by exposing internal APIs, like factoryinsight, to the internet. With this REST endpoint, users can access data stored in the UMH and seamlessly integrate Tulip with a Unified Namespace and on-premise Historian. Furthermore, the tulip-connector can be customized to meet specific customer requirements, including integration with an on-premise MES system.
How it works
The tulip-connector acts as a proxy between the internet and the UMH. It exposes an endpoint to forward requests to the UMH and returns the response.
What’s next
- Read the Tulip Connector reference documentation to learn more about the technical details of the Tulip Connector microservice.
13 - Grafana Plugins
13.1 - Umh Datasource
We are no longer maintaining this microservice. Use instead our new microservice datasource-v2 for data extraction from factoryinsight.
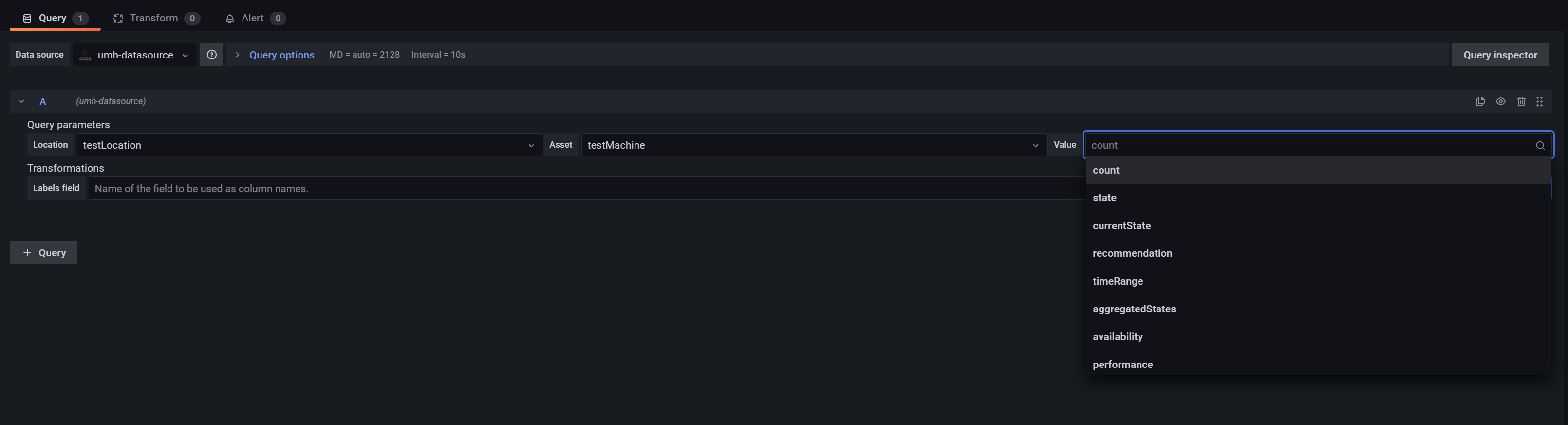
The umh datasource is a Grafana 8.X compatible plugin, that allows you to fetch resources from a database and build queries for your dashboard.
How it works
When creating a new panel, select umh-datasource from the Data source drop-down menu. It will then fetch the resources from the database. The loading time may depend on your internet speed.
Select your query parameters Location, Asset and Value to build your query.
Configuration
In Grafana, navigate to the Data sources configuration panel.
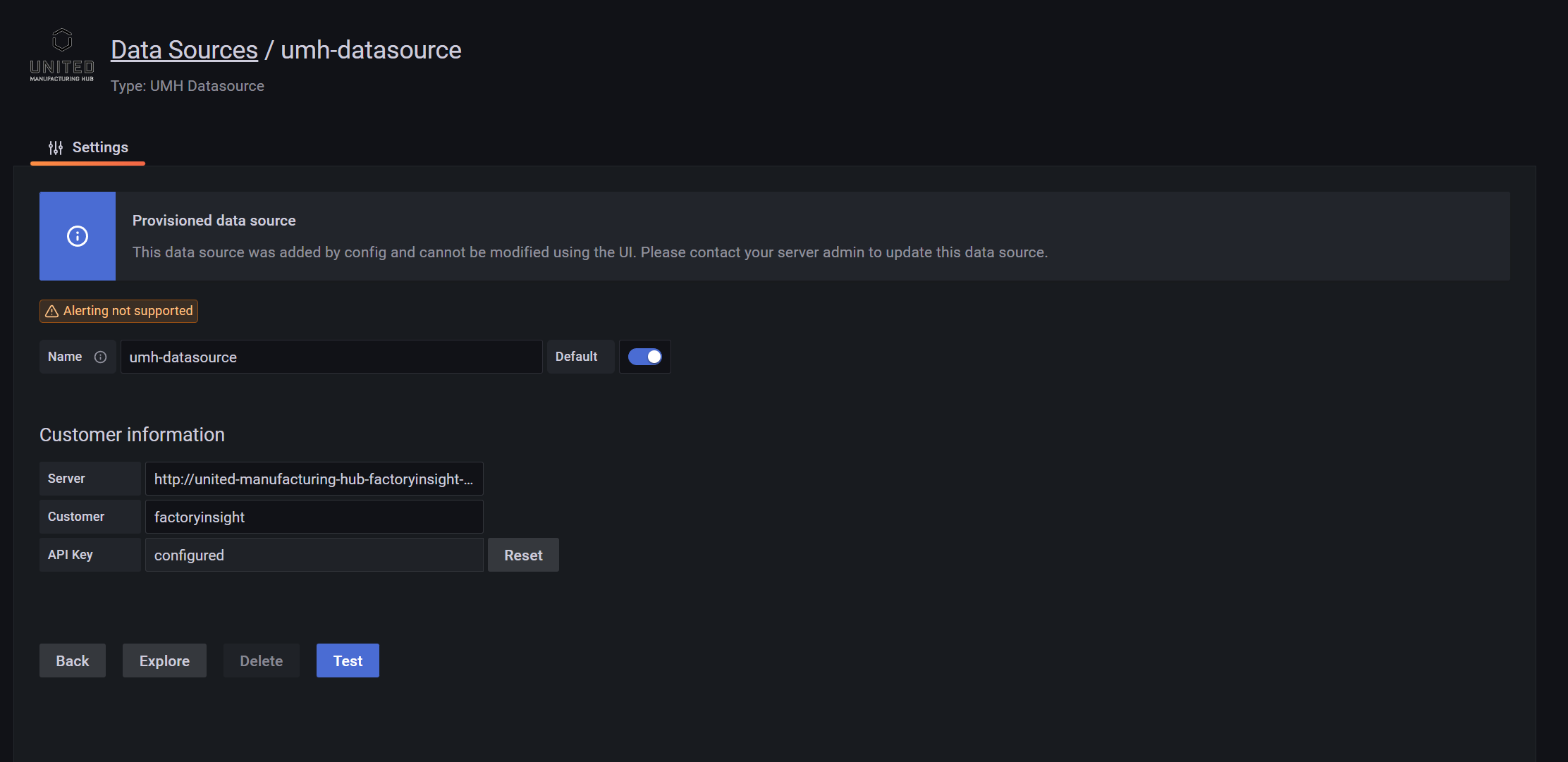
Select umh-datasource to configure it.
Configurations:
- Base URL: the URL for the factoryinsight backend. Defaults to
http://united-manufacturing-hub-factoryinsight-service/. - Enterprise name: previously customerID for the old datasource plugin. Defaults to factoryinsight.
- API Key: authenticates the API calls to factoryinsight.
Can be found with UMHLens by going to Secrets → factoryinsight-secret → apiKey. It should follow the format
Basic xxxxxxxx.
- Base URL: the URL for the factoryinsight backend. Defaults to
13.2 - Factoryinput Panel
This plugin is still in development and is not considered stable for production use
Requirements
- A United Manufacturing Hub stack
- External IP or URL to the grafana-proxy
- In most cases it is the same IP address as your Grafana dashboard.
Getting started
For development, the steps to build the plugin from source are described here.
- Go to
united-manufacturing-hub/grafana-plugins/umh-factoryinput-panel - Install dependencies.
yarn install
- Build plugin in development mode or run in watch mode.
yarn dev
- Build plugin in production mode (not recommended due to Issue 32336).
yarn build
- Move the resulting dis folder in your Grafana plugins directory.
- Windows:
C:\Program Files\GrafanaLabs\grafana\data\plugins - Linux:
/var/lib/grafana/plugins
Rename the folder to umh-factoryinput-panel.
Enable the enable development mode to load unsigned plugins.
restart your Grafana service.
Technical Information
Below you will find a schematic of this flow, through our stack.