Access the Database
4 minute read
There are multiple ways to access the database. If you want to just visualize data, then using Grafana or a database client is the easiest way. If you need to also perform SQL commands, then using a database client or the CLI are the best options.
Generally, using a database client gives you the most flexibility, since you can both visualize the data and manipulate the database. However, it requires you to install a database client on your machine.
Using the CLI gives you more control over the database, but it requires you to have a good understanding of SQL.
Grafana comes with a pre-configured PostgreSQL datasource, so you can use it to visualize the data.
Before you begin
You need to have a UMH cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by following the Getting Started guide.
You also need to access the system where the cluster is running, either by logging into it or by using a remote shell.
Get the database credentials
If you are not using the CLI, you need to know the database credentials. You can find them in the timescale-post-init-pw Secret. Run the following command to get the credentials:
sudo $(which kubectl) get secret timescale-post-init-pw -n united-manufacturing-hub -o go-template='{{range $k,$v := .data}}{{if eq $k "1_set_passwords.sh"}}{{if not $v}}{{$v}}{{else}}{{$v | base64decode}}{{end}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml
This command will print an SQL script that contains the username and password for the different databases.
Access the database using a database client
There are many database clients that you can use to access the database. Here’s a list of some of the most popular database clients:
| Name | Free or Paid | Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| pgAdmin | Free | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| DataGrip | Paid | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| DBeaver | Both | Windows, macOS, Linux |
For the sake of this tutorial, pgAdmin will be used as an example, but other clients have similar functionality. Refer to the specific client documentation for more information.
Using pgAdmin
You can use pgAdmin to access the database. To do so, you need to install the pgAdmin client on your machine. For more information, see the pgAdmin documentation.
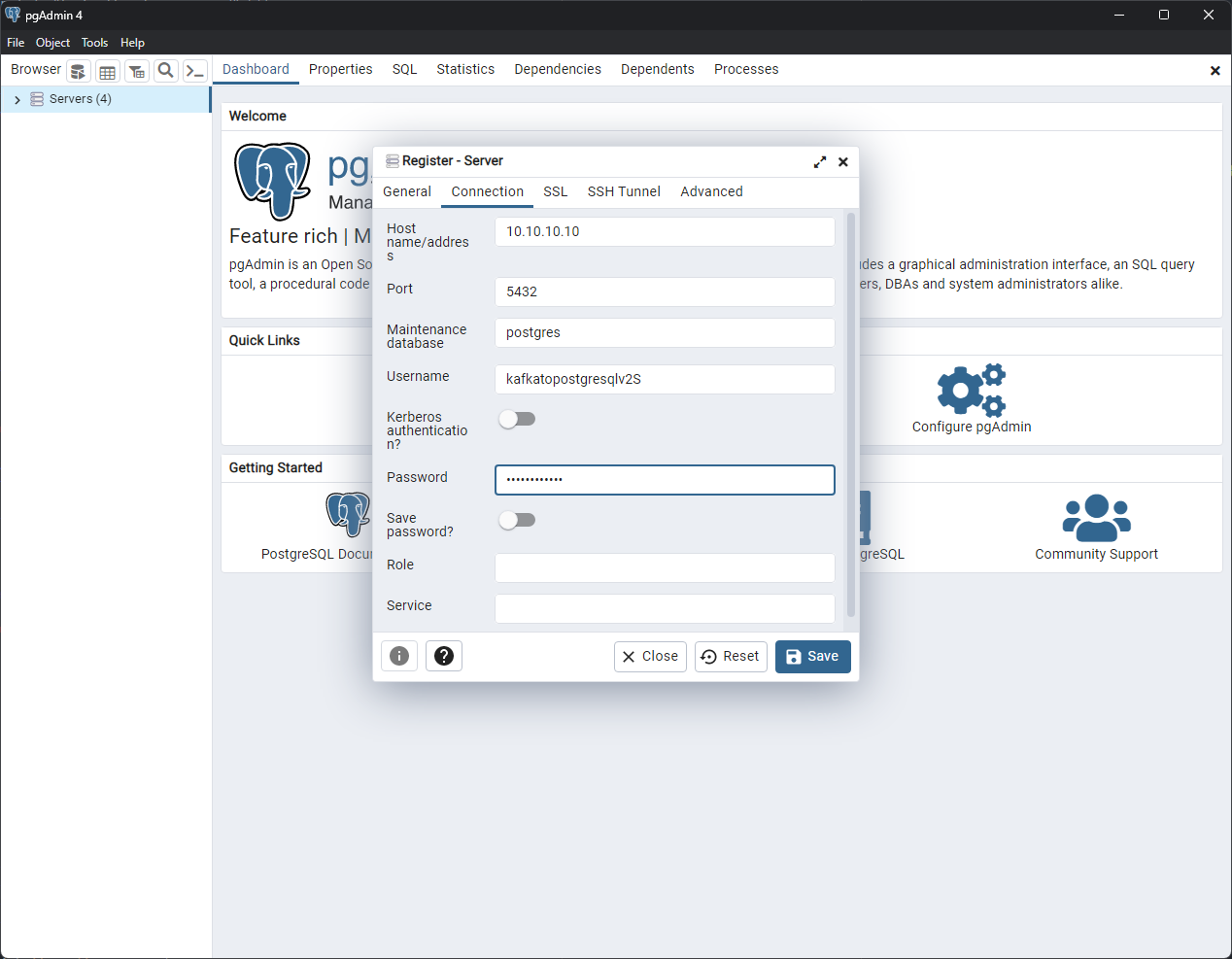
Once you have installed the client, you can add a new server from the main window.
In the General tab, give the server a meaningful name. In the Connection tab, enter the database credentials:
- The Host name/address is the IP address of your instance.
- The Port is 5432.
- The Maintenance database is postgres.
- The Username and Password are the ones you found in the Secret.
Click Save to save the server.
You can now connect to the database by double-clicking the server.
Use the side menu to navigate through the server. The tables are listed under the Schemas > public > Tables section of the factoryinsight database.
Refer to the pgAdmin documentation for more information on how to use the client to perform database operations.
Access the database using the command line interface
You can access the database from the command line using the psql command
directly from the united-manufacturing-hub-timescaledb-0 Pod.
You will not need credentials to access the database from the Pod’s CLI.
The following steps need to be performed from the machine where the cluster is running, either by logging into it or by using a remote shell.
Open a shell in the database Pod
sudo $(which kubectl) exec -it $(sudo $(which kubectl) get pods --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml -n united-manufacturing-hub -l app.kubernetes.io/component=timescaledb -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}") --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml -n united-manufacturing-hub -- psql -U postgres
This command will open a psql shell connected to the default postgres database.
Perform SQL commands
Once you have a shell in the database, you can perform SQL commands.
For example, to create an index on the processValueTable:
CREATE INDEX ON processvaluetable (valuename);When you are done, exit the postgres shell:
exit
What’s next
- See a list of SQL commands
- See how to Delete Assets from the Database
- See how to Reduce the Database Size
- See how to Backup and Restore the Database
- See how to Expose Grafana to the Internet